A SIM card is a small removable chip that is used to store data on an individual’s mobile phone. SIM is an acronym for Subscriber Identity Module. The card allows users to easily transfer information like contact lists from one phone to another. A user can even switch phones and by moving the chip, can easily transfer their phone number to a new device.

What Is a SIM Card?
Mobile phones meant for the consumers run off two primary types of technology. The first system is referred to as GSM, which stands for Global System for Mobile. The other system is called CDMA, which means Code Division Multiple Access. GSM mobile phones use SIM cards, while the other does not.
Many people ask themselves, “What is a SIM card?” Explained in the simplest terms, a SIM card is a small chip that is inserted into a GSM phone in order for it to work. Without it, a GSM phone could not connect to a mobile network. The SIM cards holds information vital to both the network provider and the user.
In the United States, most mobile phones run off of CDMA technology. This forces each phone to be tied to a specific provider and it cannot be released without the phone being unlocked. On the other end of the spectrum are the phones that run off GSM technology. A slip of the chip and all can be transferred easily. Across the globe, GSM technology is the most popular even though the U.S. does not follow the same trend.
SIM Card Work Mechanism
For such a small component, a SIM card holds a ton of data. While it stores a lot of information for the consumer, it also carries with it data vital to the mobile phone network provider.
One of the most important pieces of information the SIM card holds is the International Mobile Subscriber Identity or IMSI. The second piece of data needed to make it all work is the authentication key provided by the network provider. The key validates the IMSI, thus allowing the phone to be activated for use.
Because the data stored on the SIM card also includes login credentials, it is quite easy to switch phones. By removing the SIM card from one phone and placing into another, all your subscriber information as well as all your personal data is transferred to your new device. This is what makes GSM technology so appealing. With CDMA, the actual phone is registered to a network so there is a lot more involved when changing devices.
For added security, every SIM card has a unique identifier called the ICCID, which refers to the Integrated Circuit Card Identifier. This information is engraved on the card and includes three identifying numbers.
SIM Card Locks
A SIM lock is a feature that allows mobile network carriers to lock a phone into their specific system. Carriers often sell mobile phones at a loss to make the devices more affordable, so the only way for them to recoup their costs is by locking the phone and keeping the customer under contract for a certain time period.
Usually for a fee and once a consumer’s contract is expired, a phone’s SIM card can be unlocked. Sometimes you can buy a phone that has an unlocked SIM from the beginning, but you almost always have to pay full price for it. Software hacks can usually unlock a phone’s SIM card as well.
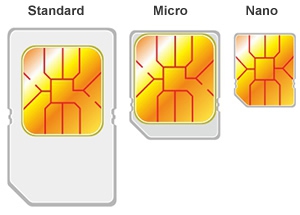
SIM Cards Sizes
Just like other things in the technology world, SIM cards come in a variety of sizes to meet an array of different uses. There are three different sizes made to accommodate different equipment. Mobile phones almost always use standard SIM card or a micro-SIM card, both of which are small enough to utilize in small devices. Standard SIM card measures 25 mm by 15 mm and micros are 15 mm by 12 mm. The first smartphone to utilize a micro-SIM card was the iPhone 4 in April 2010.
The latest development in SIM cards is the nano-SIM. It is a mere 12.3 mm x 8.8 mm in size, yet is still able to store the same amount of information as larger SIM cards. In October 2012, the iPhone 5 was the first smartphone to use the nano-SIM.
Something to keep in mind is all SIM cards are 0.76 mm thick and the microchip contacts are arranged the same. This allows smaller card to be used in place of larger ones if the proper adapter is available.
Watch the video below to learn how to cut SIM card by yourself:
How to Transfer Contacts from a SIM Card
For iPhone Users
While iPhone does not use the SIM to store contact names and phone numbers, you can still copy your contacts from a SIM card to your iPhone. Follow these steps to import the information off the SIM card:
Remove the SIM card from your iPhone and replace it with the SIM card from your old phone.
Your phone may need to reactivate. If so, connect to iTunes.
Tap Settings > Mail, Contacts, Calendars > Import SIM Contacts.
Import SIM Contacts
Remove your old SIM card from your new iPhone and reinstall the SIM card that came with it.
For Android Users
Transferring contacts from a SIM is relatively simple, and you can move them to the phone itself or back up the phone book on a module to a computer for safekeeping. Follow these steps:
Open Contacts. You can reach this from the contacts shortcut in your app drawer or home screen, or via the contacts tab in your phone dialer.
Press the Menu button.
Select Import/Export.
Select Export from SIM.
Click Select All, or manually tick each contact you wish to copy to the phone.
You may be asked where to copy the contacts to; select the appropriate option.
It takes no more than a second or two to copy over a few hundred contacts, so you'll be done in less than the time it takes to send yourself just one via SMS.
- Remember to make sure your mobile phone is fully charged before starting to transfer your contacts to your computer. When syncing data between the two devices, you can easily run down your battery because it takes a lot of power. This could jeopardize the transfer process because your data could be corrupted on both your SIM card and computer if your phone shuts down during the exchange.

View All Comments /Add Comment