A surgery done for making a hole in the ear drum, which is medically known as myringotomy, is a common surgical procedure. This surgery is usually done in combination with tympanostomy tube insertion. This tube is a small one which is placed in the ear drum hole and allows for the drainage of infectious material from the middle ear. Otolaryngologists, doctors of nose, throat and ear, are tasked with the duty of performing this procedure.
When Is Myringotomy Needed?
Otitis media with effusion (OME) is the main reason for performing myringotomy procedure. It is an infection of the middle ear with fluid. The buildup of this infectious fluid takes place behind the ear drum, becoming so thick that it is called as "glue ear." This infection can hamper hearing and if it affects both ears, it can result in slow speech development in children.
Mostly children with ages under 5 years undergo this procedure because by this age, most children have longer and wider Eustachian tubes (canal that joins the throat area with the middle ear) which allow the fluids to drain out from the ear in a better manner.
Adults rarely undergo the procedure of myringotomy with ear tube insertion. However, it happens sometimes. Barotrauma is most often the reason for adults undergoing this procedure. Barotrauma occurs because of a large pressure difference between the outside ear and the inside ear (behind the eardrum).
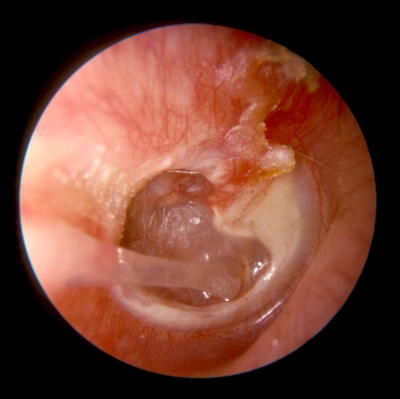
How Is Myringotomy Performed?
When performed in a hospital, the myringotomy procedure is performed under general anesthesia. The preparation of the ear marks the beginning of the procedure after the anesthesia has been administered. A solution that reduces the chances of infection is used for preparing the ear.
A sharp instrument or laser is used by the surgeon for creating a small hole in the eardrum after the ear has been prepared. The insertion of the tympanostomy tube in the hole is then carried out.
Gentle suction to the eardrum might be applied for fluid removal through the tube if the reason for the surgery is middle ear fluid. A significant amount of the fluid can be removed this way, creating an immediate improvement in hearing which can be observed after surgery. Packing the ear with gauze or cotton may be done for absorbing the drainage that might be present there.
If a single ear is to be treated, the surgery is considered complete by this stage. If the second ear is to be treated, then the same procedure is performed on it as well. The patient is then woken up by turning off anesthesia and giving some medication. While the anesthesia is wearing off, the patient is sent to the recovery room where he/she is monitored closely by the doctors.
Recovery After Myringotomy
After having undergone myringotomy, the patient is taken to the recovery room for observation while the affects of the anesthesia are wearing off. The patient is sent home if he/she wakes up feeling alert and is not experiencing any post-operative complications.
No incision is made in the skin since the procedure is performed directly on the eardrum. Thus, no incision care is needed after the surgery. You can expect to see some drainage from the ear in the first few days of the recovery period.
The drainage might be clear, blood-tinged or have a pus-like appearance. However, there is no need to worry as it is perfectly normal. However, you must make sure to protect the ear from water as it can seep into the ear through the myringotomy tubes in the same manner as the drainage seeps out of it. Earplugs might be recommended by the surgeon while swimming, having a shower or performing any activity which involves the risk of water seeping into the ear.

View All Comments /Add Comment