Human body is quite fragile and can be mutilated with ease. There is a limit to how much physical force it can bear, but it is always difficult to deal with electric force. The extent of damage usually depends on what electrical conduit you choose to grab, touch, or stick your tongue on. It also depends on how many amperes you touch.
How Many Amps Can Kill You?
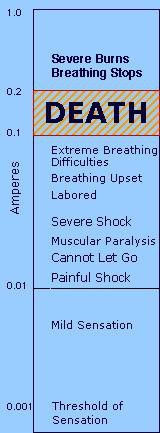
You are going to experience a painful shock by being exposed to over 10 milliamps (0.01 amps) of current.
Currents of 0.1 to 0.2 amps usually prove lethal.
Currents over 0.2 amps usually produce severe burns and unconsciousness, but immediate medical attention may help save the life of the person. Practically speaking, it is not possible to tell how much current passes through the vital organs when someone experiences an electrical shock. It is therefore important to apply artificial respiration immediately, especially if breathing has stopped.
Effects of Electrical Current on the Body
The amount of electrical current passing through the body and the length of time for which someone receives the current will determine the severity of injury from an electrical shock.
An average person can withstand 10 milliamperes (mA) of internal current and still control the muscle of the arm. Anything over 10mA is capable of paralyzing muscles, which means the person cannot release a wire, tool, or an electrified object. This results in a longer exposure to the current, which will cause serious damage. Being exposed to an electrical shock for an extended time may lead to respiratory paralysis and you stop breathing for some time. It is possible to experience respiratory paralysis from voltages as low as 49 volts.
You may experience ventricular fibrillation, or very rapid heartbeat, after being exposed to currents over 75mA. If you ask, "How many amps can kill you?" this is the answer. Ventricular fibrillation can cause death in a few minutes. It is possible to save a person if he/she receives immediate medical attention where a defibrillator is used.
It is important to understand that even if you are exposed to a lower electrical current for a long time, this will cause more damage than being exposed to a higher electrical current for a short time. Longer exposure times result in serious damage. It means 100mA applies for 3 seconds is equally dangerous as 900mA applies for 0.03 seconds. Your muscle structure will also play a role here – you are more likely to experience serious damage at lower current levels if you have less muscle tissue. Even the low voltages may prove damaging in this case.
Factors That Would Influence Effects of Electricity on Body
Volts vs. Amps
Both amperes and volts are used to describe electrical phenomena, but there is a difference.
Amperage (A): It refers to the flow of electrons through something in a second. In one amp, 6 million trillion electrons flow per second, and this flow of electron is responsible for causing damage to nervous system and tissue. These electrons can burn tissue and even interfere with electrical signals, including those that make your heart to beat.
Voltage (V): It tells you about how strong the flow of the current is. Instead of referring to the number of electrons, it refers to the push on the electrons. Zero voltage means that there is no current flow.
Electrical Resistance
Measured in ohms, an object's electrical resistance determines how much current any voltage can drive through that object. You will need more voltage to make the current pass through an object with stronger resistance. Your body also has electrical resistance, which helps protect it against electricity. The skin has a higher resistance as compared to internal tissue, which is why small shocks usually do not cause serious problem. Once the skin is breached, the effect of the same amount of amps will be severe.
Water
Your skin resists the current, but wet skin is 100 times less resistance as compared to dry skin. It is for this reason that dropping an electrical appliance of 12 volts can kill you, whereas grabbing an appliance of 12 volts with dry hands may not cause any serious damage.
Difference between AC and DC
Direct current (DC) between two points refers to a voltage that does not fluctuate, whereas a fluctuating currently will produce an alternative current (AC). In alternative current, electrons come out of an electrical outlet and then go back into it 60 times/second. There may be serious damage to the nerves from currents with 60HZ of fluctuation rate. This may cause your heart to flutter and eventually cause death. Standard AC wall current is extremely dangerous, but DC becomes dangerous when the current levels or voltage increase.

View All Comments /Add Comment